Response to Climate Change
Basic Concept
The Tsubaki Group addresses a variety of issues through its Environmental Philosophy of contributing to the “development of a sustainable society” by generating environmental value and economic value through manufacturing. In particular, the need to respond to changes in the environment is a high priority matter in the Tsubaki Group’s medium- and long-term management plans.
Climate change can present major physical risks from rising temperatures to more intense weather events. From a business perspective, while the transition to decarbonization poses a risk that could have a significant impact on the Group’s business operations, business domains, and product concepts, we recognize that the implementation of appropriate countermeasures will provide opportunities to strengthen our corporate structure, improve competitiveness, and develop new markets and business opportunities.
In recognition of these circumstances, in March 2022, the Tsubaki Group announced its support of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Utilizing the information disclosure framework recommended by the TCFD, which includes the risks and opportunities posed by climate change, we will identify and evaluate our own risks and opportunities and reflect the relevant countermeasures in our business strategies. Moreover, we will proactively disclose all relevant information related to these initiatives.

* TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures): A task force that was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) in response to a request made at the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors Meeting.
Endorsing the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
Information Disclosure in accordance with the TCFD
Activities Meant to Reduce Total CO2 Emissions
As environmental concerns persist, the Tsubaki Group is working to reduce its CO2 emissions and other greenhouse gas emissions.
In Japan, in keeping with our long-term environmental target of reducing total CO2 emissions by 46% by FY 2030 (base year: FY 2013), we are promoting specific initiatives under our voluntary environmental action program. Much of the energy used in the Group’s manufacturing is concentrated in the production process. Consequently, we are improving energy efficiency by proactively installing energy-saving production equipment; applying thermal insulation coatings to our main plants; reviewing the operating conditions of compressors; and implementing air leakage countermeasures. Furthermore, our various measures to reduce CO2 emissions include expanding the use of renewable energy by proactively installing solar power generation equipment in new and renovated plants and adopting LED lighting.
In FY 2022, we started the purchase of carbon-free power with a non-fossil certificate. In FY 2023, we acquired SBT certification and introduced internal carbon pricing (ICP), as we stepped up our efforts to promote ESG management.
FY 2022 Results
In FY 2022, the total CO2 emissions of the Tsubaki Group were as follows.
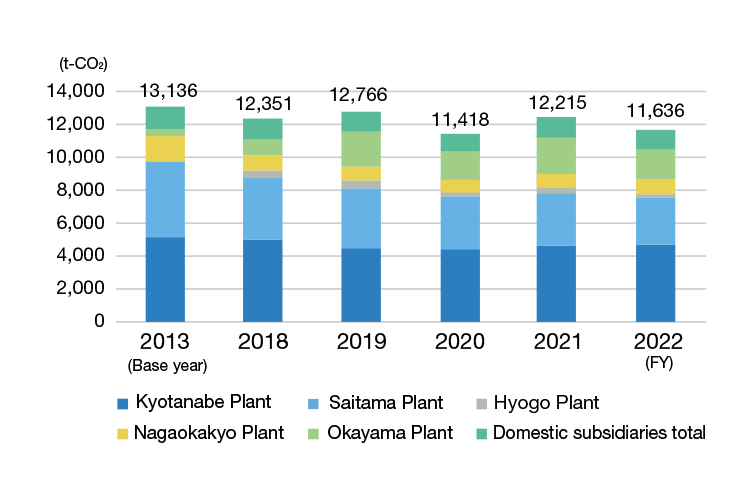
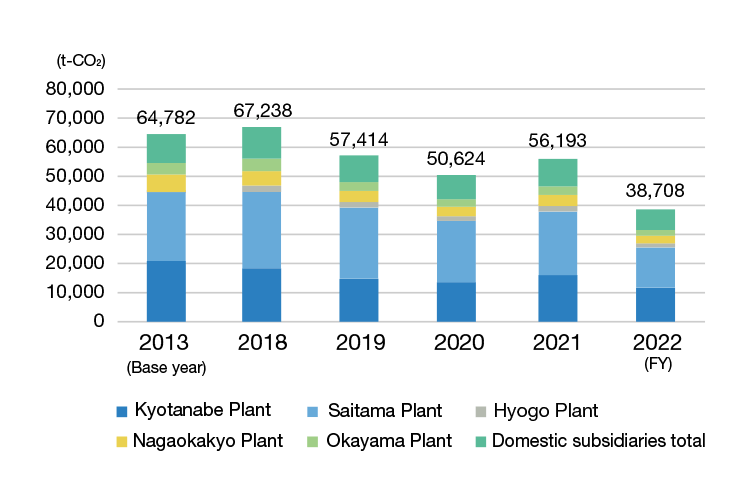
In Japan, production increased 3.9% over the previous fiscal year. However, in addition to CO2 emissions reduction measures, 10 Tsubaki Group business sites have begun purchasing carbon-free power with a non-fossil certificate. These initiatives resulted in a 31.1% reduction in total CO2 emissions. In addition, we achieved a 40.2% reduction relative to our long-term target of a 46% reduction from FY 2013 levels by FY 2030.
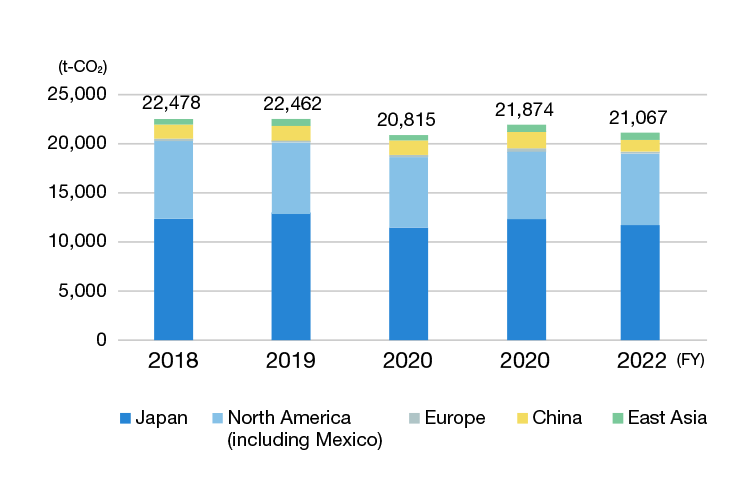
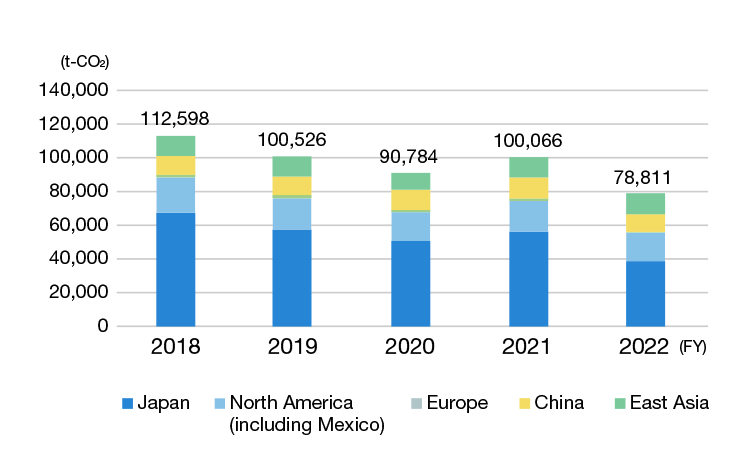
Outside Japan, we have been compiling the data from FY 2018 for our 15 major manufacturing centers located in North America, Europe, and Asia. We achieved a 11.6% reduction relative to our long-term target of a 30% reduction from FY 2018 levels by FY 2030.
Total CO2 Emissions Trend Scope 1 (CO2 Directly Emitted In-House, Such as from Fuel Consumption)
-
CO2 emissions by location (domestic)
-
CO2 emissions by location (global)
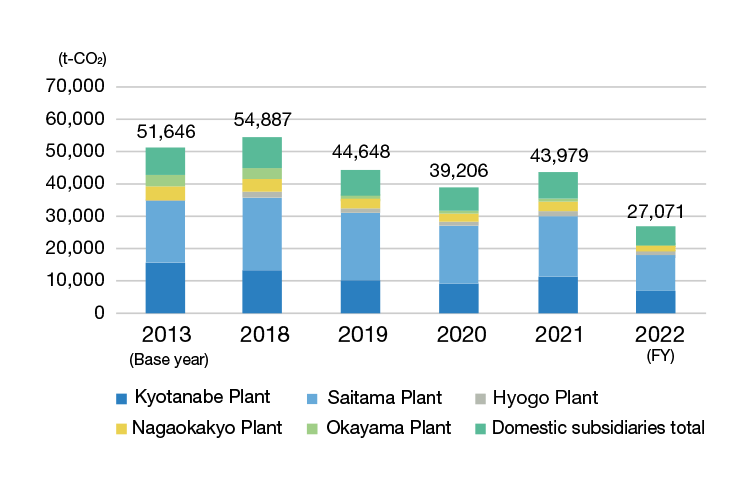
Total CO2 Emissions Trend Scope 2 (CO2 Indirectly Emitted In-House, Such as from Use of Electricity)
-
CO2 emissions by location (domestic)
-
CO2 emissions by location (global)
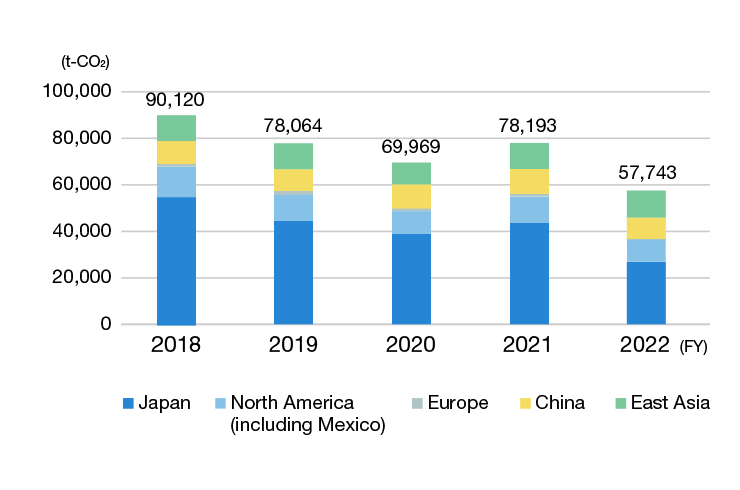
Total CO2 Emissions Trend Scopes 1 and 2
-
CO2 emissions by location (domestic)
-
CO2 emissions by location (global)
Total CO2 Emissions Scope 3 (CO2 Emitted in the Supply Chain in FY 2022)
Breakdown by category (global)
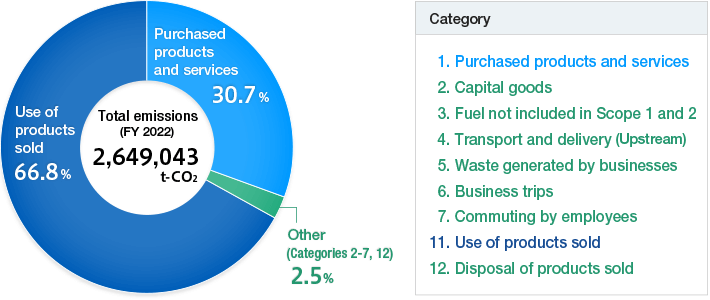
* CO2 emissions factors for domestic power use are the “alternative value” of the “emission coefficient by electric utility” published by the Ministry of the Environment.
CO2 emissions factors for power consumption outside Japan are the FY 2020 CO2 emissions factors provided in the International Energy Agency (IEA) Emissions Factors (2022 edition).
Specific Initiatives
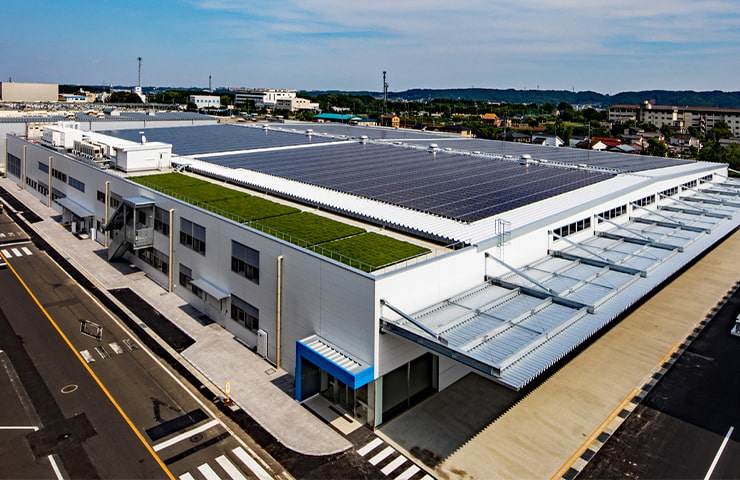

Proactive introduction of renewable energy
Whenever we build or renovate a factory building, we proactively install solar panels.
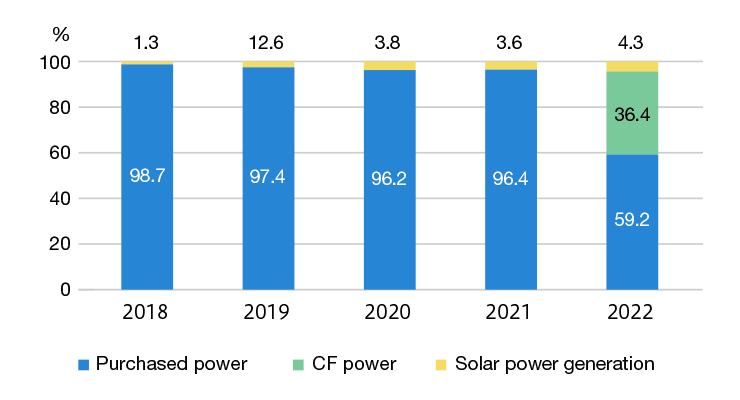
At the Saitama Plant, which is positioned as an Environmental Model Plant, through the installation of solar panels and the purchase of carbon-free power with a non-fossil certificate, we have achieved a renewable energy usage rate of about 40%.
We are also proactively promoting the increase of energy efficiency by switching to energy-saving production methods and investing in equipment, and laterally rolling out these measures across the Tsubaki Group as we work toward reducing power consumption in the entire Group.
Saitama Plant power consumption breakdown
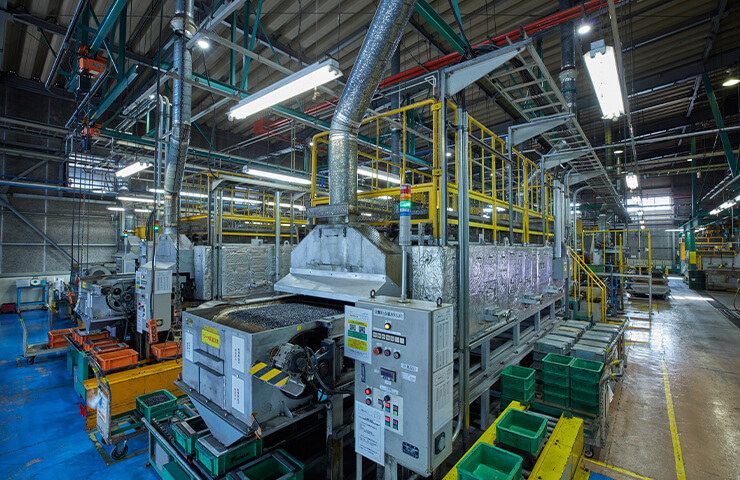

Promoting the Energy JIT Initiative in the heat treatment process
The Saitama Plant is promoting the Energy JIT Initiative in an effort to increase the energy efficiency of the heat treatment process. The JIT (just in time) Initiative is a system intended to thoroughly eliminate waste in order to produce and supply only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the quantities needed.
This system has been incorporated into several energy-efficiency initiatives, including the following:- Shutting off heaters when not needed through multiple equipment shutdowns;
- Eliminating energy waste by reviewing the timing of heat treatment furnace start-up and shutdown;
- Eliminating energy waste during holidays (heat treatment facilities typically operate 24/7); and
- Reviewing operation timing of auxiliary equipment (stopping and controlling during surplus hours)
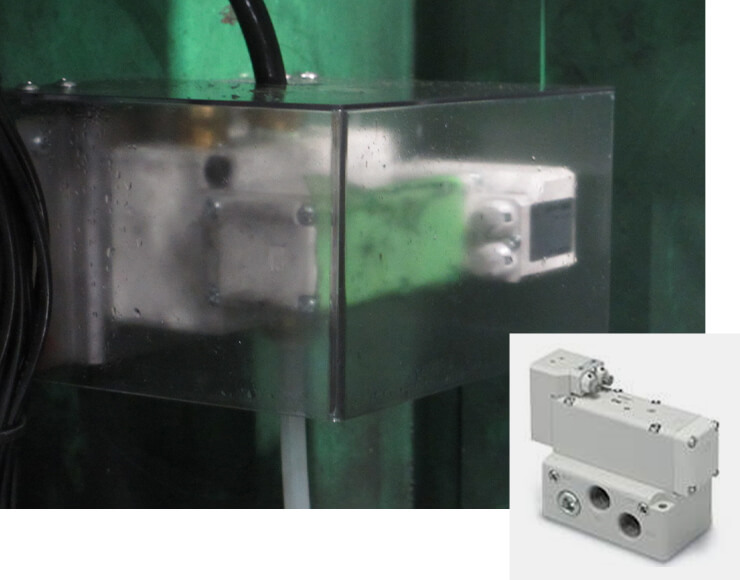

Installation of pulse blowers for air compressors
Air compressors are used for a variety of purposes in our plants. At the tensioner plant, for example, air compressors represent about 50% of the plant’s total power consumption.
In the tensioner processing line, oil and other contaminants are removed through an air-blowing process after the regular operation and cleaning processes. We have since adopted a pulsed blowing system. This allows the same functionality to be achieved with about half the air consumption, resulting in significant energy saving.
We are working to reduce power consumption at our other plants by deploying this system as needed.
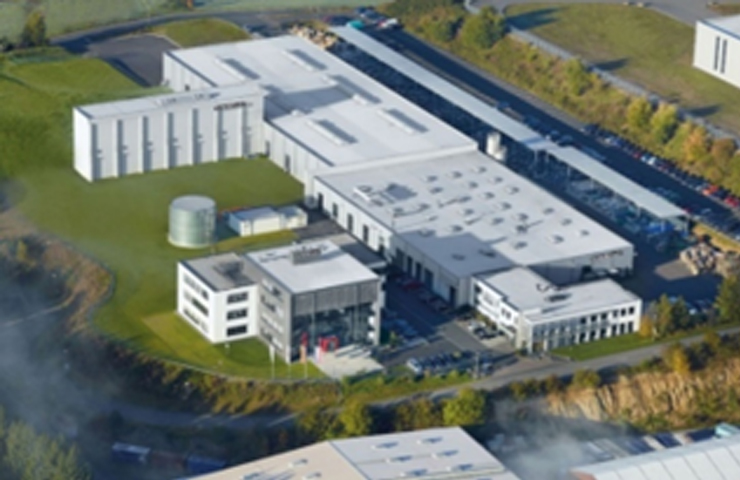

Examples of initiatives at overseas group company
Tsubaki Kabelschlepp GmbH (Germany)
Tsubaki Kabelschlepp GmbH is actively implementing CO2 reduction activities to achieve their long-term environmental goals.
For example:- Optimizing resource efficiency (Waste heat recovery from compressors and injection molding)
- Switching to renewable energy
(Switch to 100% renewable energy from January 2022) - Using LED lighting (completed in all production areas)
- Replacing existing equipment with high efficiency equipment (Planned equipment replacement with high efficiency injection molding machines)