Priority Matters and Indicators of Sustainability
At the Tsubaki Group, we first set priority matters (material issues) and indicators (KPIs) from the CSR side under our Basic Policy on Sustainability. (See the identifying process below.)
With regard to the social issues that will be resolved through our core business (our products)—namely, CSV issues—we have listed them as priority matters under our Long-term Vision 2030 and Mid-term Management Plan 2025 and are addressing them from a medium- to long-term perspective.
These initiatives contribute directly to the SDGs, and clarifying the relationship between them will help raise employees’ awareness thereof.
Process for Identification of Material Issues (Priority Matters) Regarding Sustainability
1. To identify material issues from the dual perspectives of risks and opportunities regarding sustainability, responsible divisions identified and evaluated their own issues leveraging the 17 SDGs.
2. Defined and evaluated risks and opportunities based on their importance to stakeholders and importance to the Company (including the gap between what the Company currently is and what it strives to be), using the matrix on the right.
3. In light of the above, the sustainability-related divisions will consider the importance of the Group as a whole, and the Sustainability Committee will make a final decision regarding material issues.
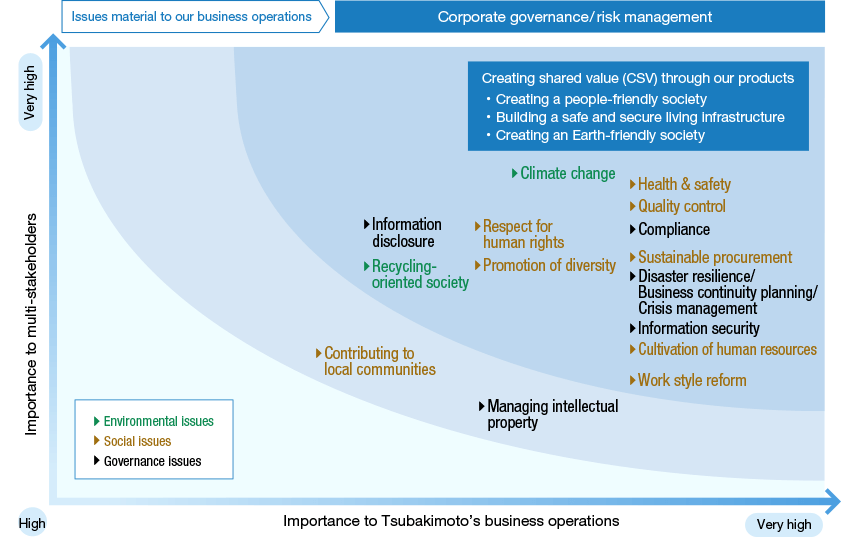
Material Issues (Priority Matters) and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)
| Material Issues (Priority Matters) |
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) |
Contribution to the SDGs |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| E (Environment) |
1. Climate change | CO2 total emissions reductions (reference year FY 2013) |
|
| CO2 total emissions reductions (reference year FY 2018) | |||
| Ratio of renewable energy consumption | |||
| CDP climate change score | |||
| 2. Recycling-oriented society | Waste recycling rate | ||
| PRTR-substance emissions *1 | |||
| Number of violations of environmental laws and regulations | |||
| S (Society) |
3. Respect for Human Rights/Promotion of Diversity | Number of companies implementing ethics education |
|
| Number of companies implementing due diligence regarding respect for human rights | |||
| Ratio of employees with disabilities | |||
| Ratio of companies meeting legally required employment ratios for people with disabilities | |||
| Number of non-Japanese employees | |||
| Ratio of senior female employees | |||
| 4. Cultivation of human resources/Workstyle reforms | Education plan implementation rate | ||
| Ratio of paid leave acquisition | |||
| Ratio of maternity and childcare leave-takers who have returned to work | |||
| Ratio of employees with high level of stress | |||
| 5. Health & safety | Number of lost time accidents | ||
| 6. Quality assurance | Number of major quality issue occurrences *2 | ||
| 7. Contribution to local communities | - | ||
| 8. Sustainable procurement | Number of companies to which we have delivered carbon neutrality initiatives webinars |
||
| Ratio of companies implementing status surveys of CO2 emission reductions initiatives | |||
| Number of sustainability guidelines issued | |||
| G (Governance) |
9. Compliance | Number of serious violations of Company regulations |
|
| Number of companies that participated in Corporate Ethics Awareness Month | |||
| 10. Disaster resilience/Business continuity planning/Crisis management | Ratio of business sites implementing disaster prevention and evacuation drills | ||
| Number of business sites revising their business continuity plans (BCPs) | |||
| 11. Information security | Number of serious system incident occurrences | ||
| Number of information security accident occurrences | |||
| 12. Information disclosure | - | ||
| 13. Managing intellectual property | Number of valid warnings received claiming infringement of intellectual property rights | ||
Scope: (within Japan) Tsubakimoto Chain and domestic consolidated subsidiaries; (global) major subsidiaries both domestic and overseas
*1: PRTR: Pollutant Release and Transfer Register
*2: According to an internally established definition