Risk Management
Basic Concept
To sustain and continuously grow our business, it is essential that we fulfill our corporate social responsibilities and effectively manage various risks inherent in our operations.
The Tsubaki Group has established a Basic Risk Management Policy to minimize potential losses, by continually identifying and assessing risk factors that could significantly affect our management and operations.
Basic Risk Management Policy
Tsubakimoto Chain Co. and its group companies in both Japan and abroad have established the following principles to prevent potential risks that may have material adverse effects on the business management of the Tsubaki Group and to minimize damage if a risk does occur. The Tsubaki Group strives to become resilient to risks and to maintain the public trust and confidence that it has enjoyed.
1. We will identify, analyze, and assess risks associated with global business activities and take efficient and effective risk control measures. We will regularly monitor how the measures are being taken and make improvements where necessary.
2. We will have a risk management system in place and take continuous measures with a focus on risk prevention. We will ensure that the risk management system is well communicated throughout the Group and work as a team toward accomplishing a goal.
3. We will provide education and training to employees to raise their risk awareness and risk response skills so that risk management becomes a part of their routine.
4. In the event of a disaster, accident, or other emergency situations, we will promptly set up an emergency task force. With safety of life as the highest priority, we will work closely with the local community, take actions, and conduct recovery operations promptly.
5. We will adapt risk control measures to best suit the specific requirements of the country or region.
Established: September 2003
Revised: November 2013
Promotion System
The Tsubaki Group has established specialized committees on corporate ethics; information security; the environment; quality; health and safety; and compliance and crisis management. These committees operate under the supervision of the Sustainability Committee to ensure effective and efficient risk management. In close coordination with the departments responsible for overseeing risks, we promote the implementation of Group-wide countermeasures that focus on identifying and evaluating risk factors and preventing risks before they occur.
In addition, we have established a global emergency contact system to minimize potential losses in the event of a risk materializing.
Principal Initiatives
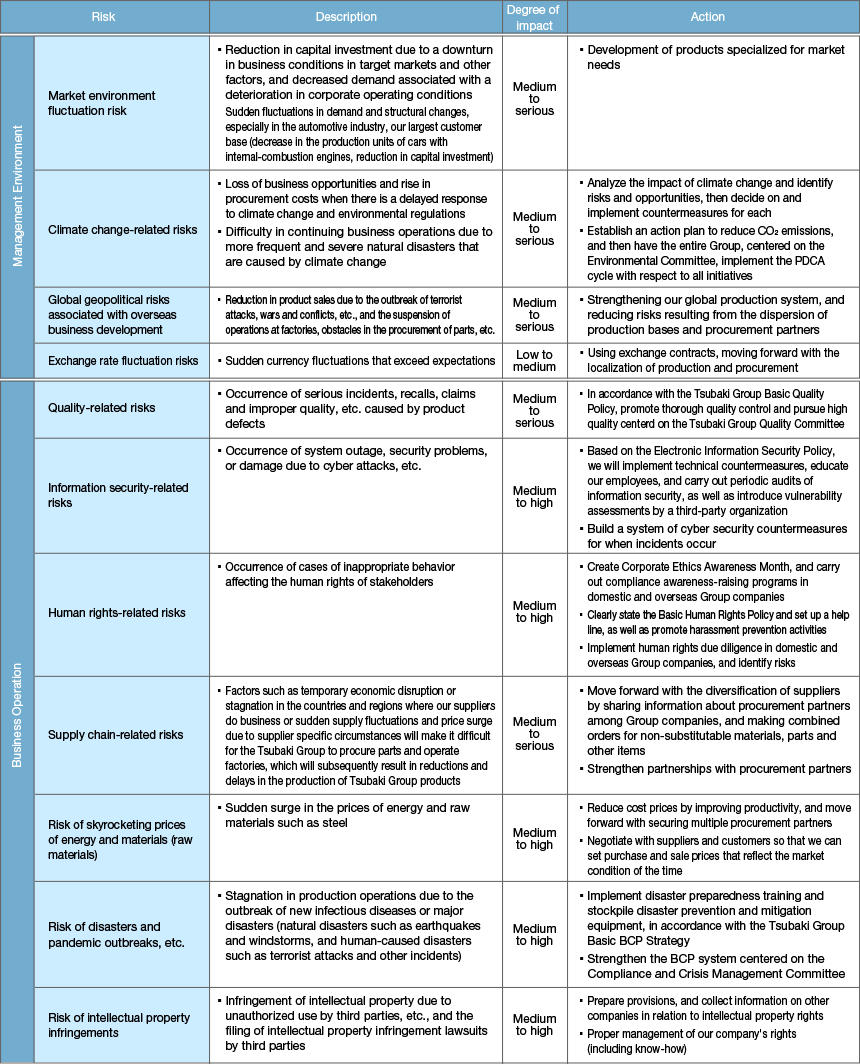
The Tsubaki Group regularly evaluates the risks faced by each Group company and reviews the status of response measures. Committees on corporate ethics, information security, the environment, quality, health and safety, and compliance and crisis management carry out targeted risk management initiatives in their respective areas based on these evaluations.
In FY 2024, we concentrated on seven key areas: addressing climate change, managing human rights and labor-related risks, managing supply chain risks, enhancing of crisis management systems, bolstering cyber security measures, as well as ensuring health and safety, and quality assurance.
These activities are reported to the Sustainability Committee, which provides necessary guidance or instructions at appropriate intervals.
Business Continuity Planning/Disaster Preparedness Initiatives
To prepare for natural disasters, incidents, and other large-scale emergencies that have become increasingly common in recent years, the Tsubaki Group has established a Basic BCP Policy and is implementing a range of disaster preparedness initiatives.
(BCP: Business Continuity Plan)
(1) Business continuity plan revision initiatives
Since FY 2022, Tsubaki has been revising its business continuity plans not only at its own sites but also across other Group companies in Japan. The goal is for each business division and the General Affairs Department to work together to ensure the early restoration of business activities in the event of an emergency, while placing the highest priority on protecting human life. In addition, we are holding BCP seminars for officers and members of the Crisis Management Committee, and strengthening the systems necessary to support effective crisis response.
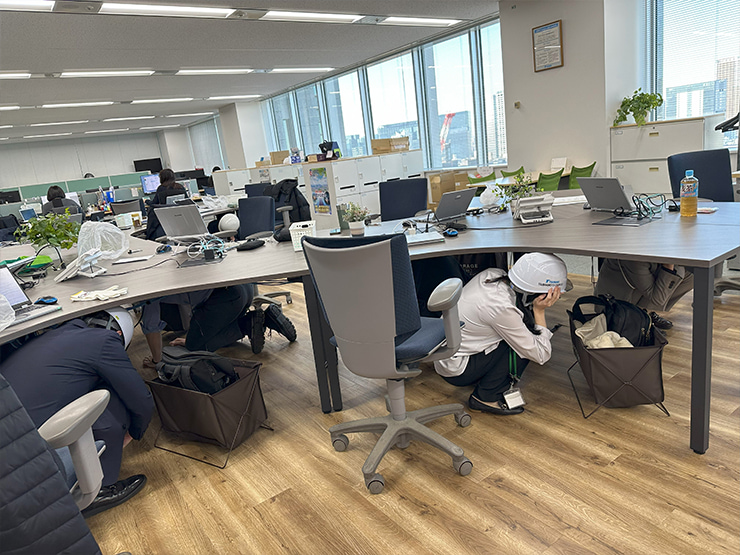
(2) Disaster preparedness drills
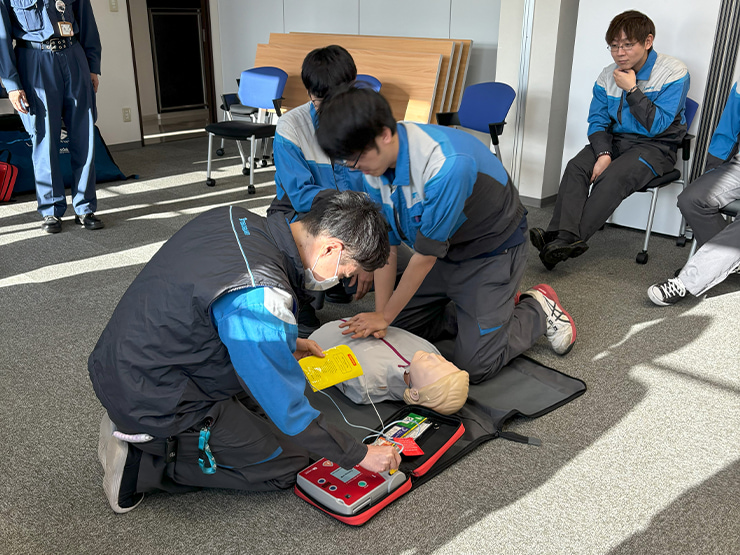
We conduct evacuation and fire-fighting drills at least once a year for both daytime and night-shift employees, covering a range of work schedules to reflect possible disaster scenarios. In FY 2024, we held evacuation drills and medical emergency training at the Tokyo Office, Nagoya Office, Toyota Sales Office, and North Osaka Sales Office, all located in high-rise buildings. In addition, we are strengthening voluntary activities in order to raise employee awareness of disaster preparedness.
(3) Utilization of the safety confirmation system
To confirm the safety of employees and their families quickly in the event of a serious disaster such as an earthquake, typhoon, torrential rain, or heavy snowfall, we have introduced a smartphone-based safety confirmation system. Through regular drills, we have strengthened our ability to rapidly verify employee safety and assess damage during emergencies such as earthquakes.
(4) Installation of equipment for disaster preparedness, disaster mitigation, and use in emergencies
We are stockpiling water, food, simple toilet liner bags, blankets, lanterns, dedicated emergency telephones, and other supplies at each business site to support employees who may be unable to return home during a disaster.
As an emergency power source in the event of an outage, we have installed emergency generators and eLINK* V2X bi-directional EV charging systems in the welfare buildings at our plants in Japan. These measures ensure that the functions of the Disaster Response Headquarters can be maintained and that meals can be provided to employees unable to return home.
* eLINK: Bidirectional charging system for sending and receiving electrical power between a building and EV (our company’s product). In addition to EV charging, the power stored in the EV battery can be supplied to other locations.
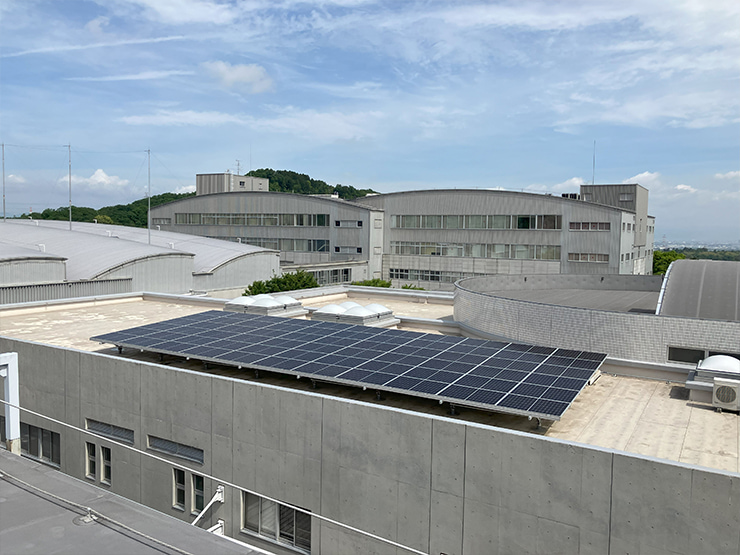
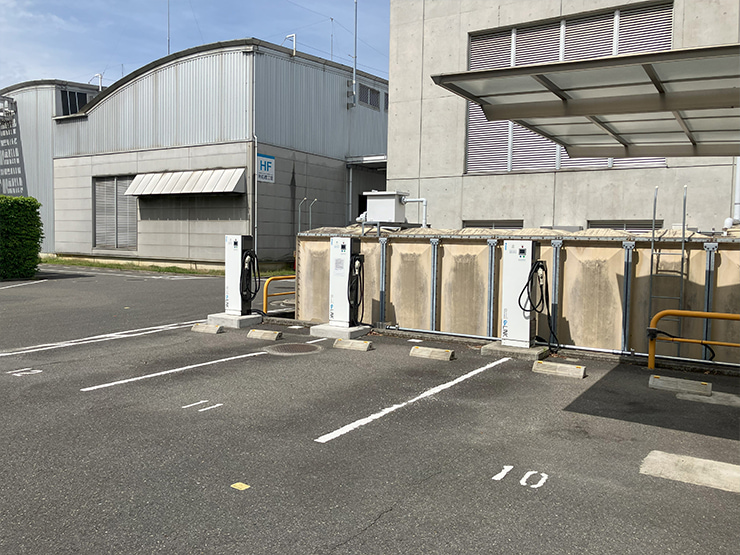


At the Kyotanabe Plant, solar power generation equipment and eLINK have been integrated to establish a system that supplies power to the welfare building in the event of a power outage
(Normally, environmental impact is reduced through the use of solar power generation (renewable energy))